Different evolutionary constraints on CheW and CheY proteins revealed by heterologous expression studies and protein sequence analysis
Abstract
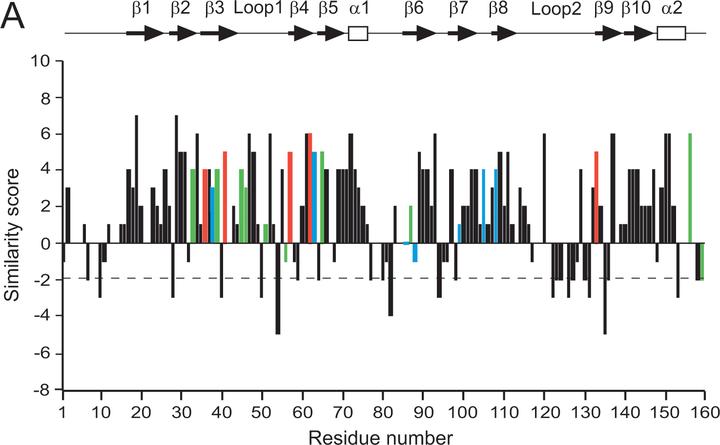
CheW and CheY are single-domain proteins from a signal transduction pathway that transmits information from transmembrane receptors to flagellar motors in bacterial chemotaxis. In various bacterial and archaeal species, the cheW and cheY genes are usually encoded within homologous chemotaxis operons. We examined evolutionary changes in these two proteins from distantly related proteobacterial species, Escherichia coli and Azospirillum brasilense. We analyzed the functions of divergent CheW and CheY proteins from A. brasilense by heterologous expression in E. coli wild-type and mutant strains. Both proteins were able to specifically inhibit chemotaxis of a wild-type E. coli strain; however, only CheW from A. brasilense was able to restore signal transduction in a corresponding mutant of E. coli. Detailed protein sequence analysis of CheW and CheY homologs from the two species revealed substantial differences in the types of amino acid substitutions in the two proteins. Multiple, but conservative, substitutions were found in CheW homologs. No severe mismatches were found between the CheW homologs in positions that are known to be structurally or functionally important. Substitutions in CheY homologs were found to be less conservative and occurred in positions that are critical for interactions with other components of the signal transduction pathway. Our findings suggest that proteins from the same cellular pathway encoded by genes from the same operon have different evolutionary constraints on their structures that reflect differences in their functions.