The 3.2 A resolution structure of a Receptor:CheA:CheW signaling complex defines overlapping binding sites and key residue interactions within bacterial chemosensory arrays
Abstract
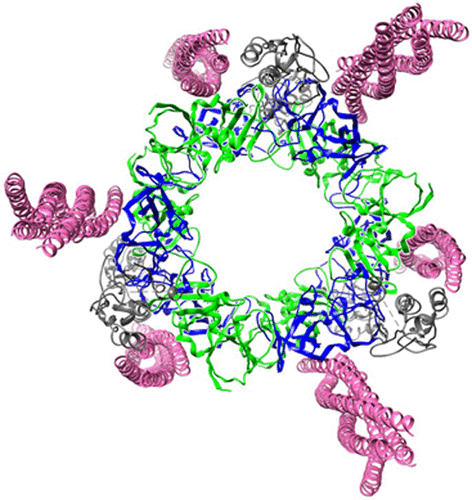
Bacterial chemosensory arrays are composed of extended networks of chemoreceptors (also known as methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins, MCPs), the histidine kinase CheA, and the adaptor protein CheW. Models of these arrays have been developed from cryoelectron microscopy, crystal structures of binary and ternary complexes, NMR spectroscopy, mutational, data and biochemical studies. A new 3.2 Å resolution crystal structure of a Thermotoga maritima MCP protein interaction region in complex with the CheA kinase-regulatory module (P4–P5) and adaptor protein CheW provides sufficient detail to define residue contacts at the interfaces formed among the three proteins. As in a previous 4.5 Å resolution structure, CheA-P5 and CheW interact through conserved hydrophobic surfaces at the ends of their β-barrels to form pseudo 6-fold symmetric rings in which the two proteins alternate around the circumference. The interface between P5 subdomain 1 and CheW subdomain 2 was anticipated from previous studies, whereas the related interface between CheW subdomain 1 and P5 subdomain 2 has only been observed in these ring assemblies. The receptor forms an unexpected structure in that the helical hairpin tip of each subunit has “unzipped” into a continuous α-helix; four such helices associate into a bundle, and the tetramers bridge adjacent P5-CheW rings in the lattice through interactions with both P5 and CheW. P5 and CheW each bind a receptor helix with a groove of conserved hydrophobic residues between subdomains 1 and 2. P5 binds the receptor helix N-terminal to the tip region (lower site), whereas CheW binds the same helix with inverted polarity near the bundle end (upper site). Sequence comparisons among different evolutionary classes of chemotaxis proteins show that the binding partners undergo correlated changes at key residue positions that involve the lower site. Such evolutionary analyses argue that both CheW and P5 bind to the receptor tip at overlapping positions. Computational genomics further reveal that two distinct CheW proteins in Thermotogae utilize the analogous recognition motifs to couple different receptor classes to the same CheA kinase. Important residues for function previously identified by mutagenesis, chemical modification and biophysical approaches also map to these same interfaces. Thus, although the native CheW–receptor interaction is not observed in the present crystal structure, the bioinformatics and previous data predict key features of this interface. The companion study of the P5-receptor interface in native arrays (accompanying paper Piasta et al. (2013) Biochemistry, DOI: 10.1021/bi400385c) shows that, despite the non-native receptor fold in the present crystal structure, the local helix-in-groove contacts of the crystallographic P5-receptor interaction are present in native arrays and are essential for receptor regulation of kinase activity.